Relevant Products
Embedded terminal templates and Card conversions are available in BREEZE MFD pro mfp
When you add a new card conversion or edit an existing one, you can specify card number pairs and find a defined conversion or enter a new conversion
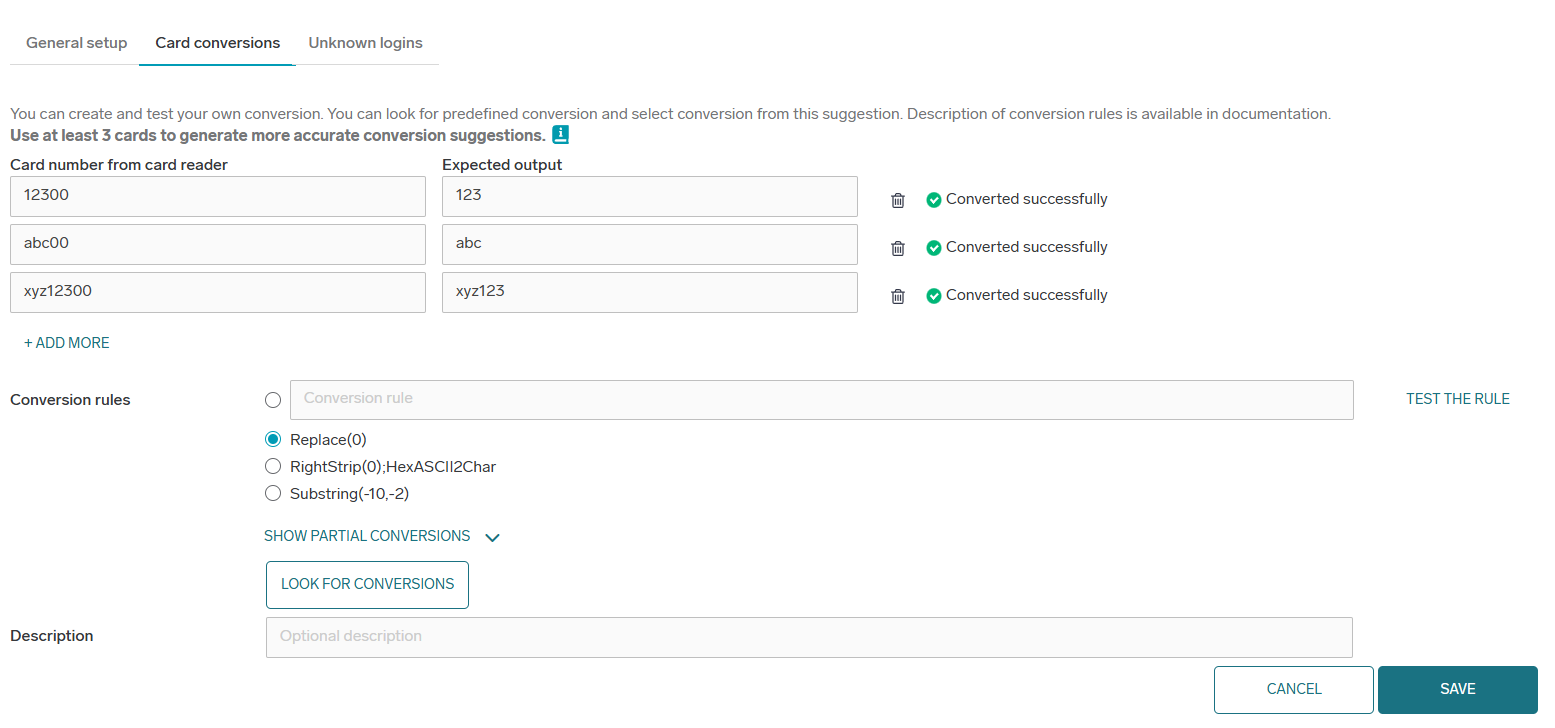
The more card number pairs you enter, the more exact results you get. You should enter at least three different pairs to get a valid result. You can test the selected rule to verify that all entered card numbers are correctly converted.
You can also specify your own conversions
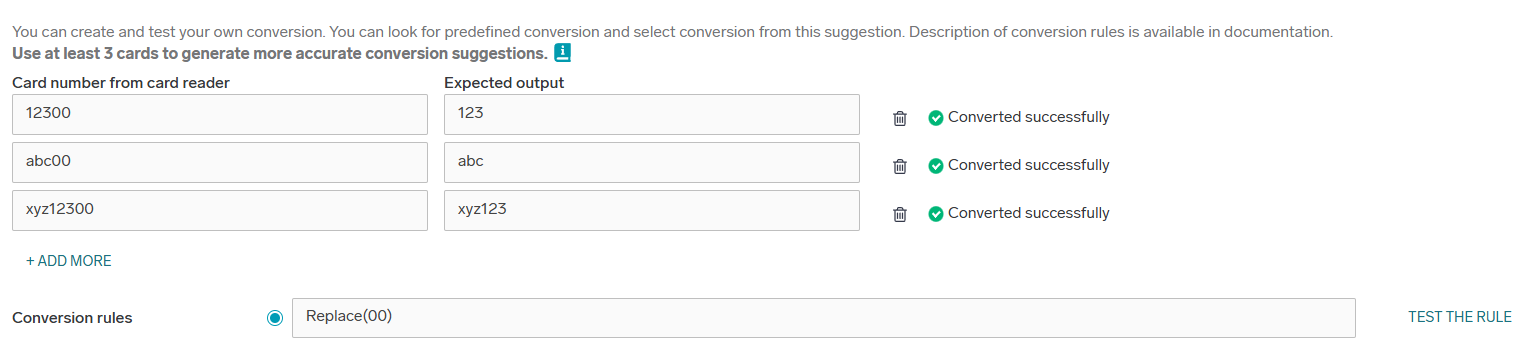
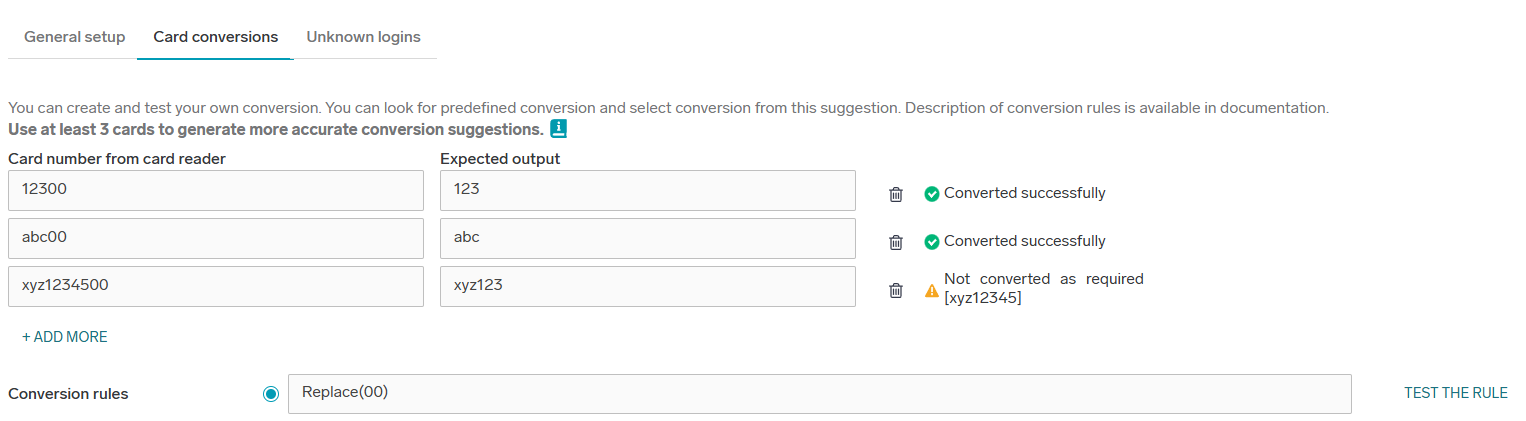
In case the selected conversion does not convert all cards successfully, you are notified about it.
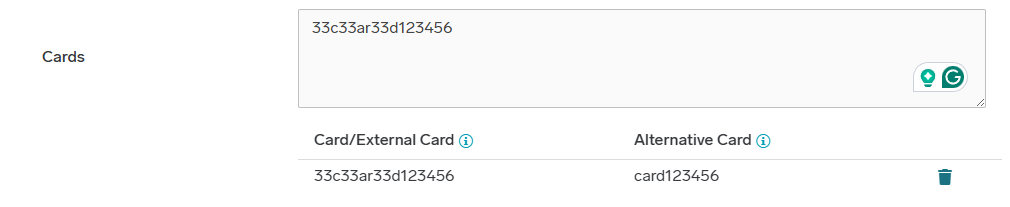
Alternative cards
When the card conversion is used, an alternative card is saved to the user. In the user detail, you can see all his alternative cards. For example, this alternative card was created with existing conversion LowerCase;Replace(d,33d);Replace(c,33c);Replace(b,33b);Replace(a,33a);Replace(e,33e);Replace(f,33f) when the original card 33c33ar33d123456 was read from another terminal as card123456.
For more details on how the conversions work, continue reading below.
Limitations
-
When there are some alternative cards saved for an external user and the card saved in the external provider is reassigned to another user, the following happens upon the next card login
-
If the new user already existed in HCP (he had already logged in before), all alternative cards related to the external card are reassigned to the new user
-
If the new user did not exist in HCP before (first login), no alternative cards are reassigned, they are only deleted. Upon next login, the alternative cards are created.
-
The Conversion Function
|
SAFEQ Cloud supports conversions of card numbers as read by the card reader at Terminal. A typical conversion configuration looks as follows:
Each rule is represented by its name (see the description of rules) and separated by a semicolon. Some rules have one or two parameters which are in parentheses and separated by a comma.
Some conversions may contain two (or more) independent conversion rules that are connected by the operator '+'. The conversion is executed from the left, rule by rule. Each conversion rule takes the last converted number and executes. Where the operator '+' appears, it takes the output from a preceding rule, executes the rules in parallel, and returns the results of both rules. The result in the case of operator '+' may look as follows: Conversion rule: |
A Description of Rules
The following rules are sorted alphabetically.
Please note that rule names are CASE SENSITIVE.
|
ASCII2Hex |
This rule converts a string in ASCII format (typically from a KM reader) into hex form. The other input is not changed. ASCII format is "^([34][0-9])+([fF]{2})*$"
|
|
Bin2Dec |
Converts a number from binary format into decimal format.
|
|
CardNo |
Returns original card number. Could be used with operator +. Syntax:
Examples:
|
|
Const |
Returns a specified string. Could be used with the operator '+'. Similar functionality provides LeftAppend and RightAppend.
|
|
Dec2Bin |
Converts a number from decimal format into binary format.
|
|
Dec2Hex |
Converts a number in decimal format into hexadecimal format
|
|
DecimalAdd |
Adds a value in decimal format to a current value in decimal format
|
|
DecimalAnd |
Makes binary AND. Mask is in decimal format.
|
|
DecValue2Hex |
Inversion function to Hex2DecValue. Converts each pair of decimal number to a hexadecimal digit. (08 -> 8, 11 -> B). The input must have an even length. Example:
|
|
Hex2ASCII |
This is the inverse function to ASCII2Hex. Converts a hexadecimal string into an ASCII representation. The input string could have a maximum length of 16 signs. Otherwise, the original input is returned.
|
|
DESDecrypt |
Decodes a value encrypted by DES in Base64 format. Example:
|
|
DESEncrypt |
Encodes a value into DES and Base64 format. Example:
|
|
Hex2ASCII |
Converts a hex number to its ASCII representation. It is the inversion function to ASCII2Hex; Example:
|
|
Hex2Dec |
Converts a number from hexadecimal format into decimal format.
|
|
Hex2DecValue |
Converts each hexadecimal digit into a decimal representation (8 – 08, A – 10, B – 11, etc.).
|
|
Hex2Oct |
Converts a number from hexadecimal format into octal format.
|
|
HexAnd |
Makes binary AND. Mask is in hexadecimal format. DecimalAnd contains similar functionality.
|
|
IsEmbed |
Allow next processing only if a card number is from an embedded reader.
|
|
IsEven |
Allow next processing only if a card number length is even.
|
|
IsEvenEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is even else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator. Syntax:
Examples:
|
|
IsLength |
Allows next processing only if the card number length is equal to a specified value.
|
|
IsLengthEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is equal to specified value else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator. Syntax:
Example:
|
|
IsLengthGreater |
Allow next processing only if the card number length is greater than a specified value.
|
|
IsLengthGreaterEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is greater than specified value else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator.
Examples:
|
|
IsLengthNot |
Allow next processing only if the card number length is different to a value.
|
|
IsLengthNotEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is different from value else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator.
Examples:
|
|
IsLengthSmaller |
Allow processing of next rules (until operator "+") only if card number length is smaller than the specified value.
Examples:
|
|
IsLengthSmallerEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is smaller than specified value else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator.
Examples:
|
|
IsNotStartWith |
Allow next processing only if the card number does not start with a specified string.
|
|
IsNotStartWithEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number doesn't start with specified string else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator.
Examples:
|
|
IsOdd |
Allow processing of next rules (until operator "+") only if card number length is odd.
Examples:
|
|
IsOddEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number length is odd else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator. Syntax:
Examples:
|
|
IsStartWith |
Allow next processing only if the card number starts with a specified string. Syntax:
Example:
|
|
IsStartWithEE |
Allow processing of next rules only if card number starts with specified string else empty current output and skip to next "+" operator. Syntax:
Examples:
|
|
LeftAppend |
Appends a specified string from the left side. RightAppend has similar functionality.
|
|
LeftCut |
Cuts a specified prefix from left. If the prefix does not match, then do nothing.
|
|
LeftHexShift |
Unary bit operation LEFT SHIFT for a specified count of bits. Input and output are in hexadecimal format. This operation is equivalent to multiplying by 2count
|
|
LeftPadding |
Pads with a specified sign from left to a specified length.
|
|
LeftShift |
Unary bit operation LEFT SHIFT for a specified count of bits. Input and output are in decimal format. LeftHexShift has similar behavior. This operation is equivalent to multiplying by 2count
|
|
LeftStrip |
Strips a specified sign from left.
|
|
LowerCase |
Convert san alphabetical sign to its lowercase representation.
|
|
LRC |
Computes a Longitudinal Redundancy Check http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longitudinal_redundancy_check and adds it to the end. Example:
|
|
MD5 |
Computes an MD5 hash of input. Example:
|
|
Replace |
Replaces all occurrences of one sequence with another one.
|
|
Reverse2 |
Byte reverse – it is useful only for a hexadecimal input because 2 signs represent one byte. Therefore, this operation makes a reverse string by pair. Even the length is necessary.
|
|
Reverse |
Reverse of string.
|
|
RightAppend |
This function is similar to LeftAppend. Append a specified string from the right side.
|
|
RightHexShift |
Unary bit operation RIGHT SHIFT for a specified count of bits. Input and output are in hexadecimal format. This operation is equivalent to dividing by 2count
|
|
RightPadding |
Pads with a specified sign from right to a specified length.
|
|
RightShift |
Unary bit operation RIGHT SHIFT for a specified count of bits. Input and output are in decimal format. RightHexShift has similar behavior. This operation is equivalent to dividing by 2count
|
|
RightStrip |
Strips a specified sign from the right.
|
|
SignReverse |
This conversion takes every string in hexadecimal format and makes its binary reverse. For example, (5 is represented in binary as 0101, reverse transfer it into 1010 that is A)
|
|
Substring |
Selects a substring of the input. If any argument is negative, then it is used from the right side (from the end).
|
|
Swap12785634 |
Swap 4th byte with 2nd. It is only useful for hexadecimal format.
|
|
SwapPair |
Swaps even and odd signs.
|
|
UpperCase |
Converts an alphabetical sign into its uppercase representation.
|
